
However, the starting nucleus is always diploid and the nuclei that result at the end of a meiotic cell division are haploid.

Meiosis employs many of the same mechanisms as mitosis. In mitosis, both the parent and the daughter nuclei contain the same number of chromosome sets-diploid for most plants and animals. As you have learned, mitosis is part of a cell reproduction cycle that results in identical daughter nuclei that are also genetically identical to the original parent nucleus. The nuclear division that forms haploid cells, which is called meiosis, is related to mitosis. Gametes fuse with another haploid gamete to produce a diploid cell. In animals, haploid cells containing a single copy of each homologous chromosome are found only within gametes.
#CHIASMATA CROSSOVER DEFINITION FULL#
Diploid organisms inherit one copy of each homologous chromosome from each parent all together, they are considered a full set of chromosomes.

Homologous chromosomes are matched pairs containing genes for the same traits in identical locations along their length. Somatic cells are sometimes referred to as “body” cells. Most animals and plants are diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes in each somatic cell (the nonreproductive cells of a multicellular organism), the nucleus contains two copies of each chromosome that are referred to as homologous chromosomes. So, in addition to fertilization, sexual reproduction includes a nuclear division, known as meiosis, that reduces the number of chromosome sets. If the reproductive cycle is to continue, the diploid cell must somehow reduce its number of chromosome sets before fertilization can occur again, or there will be a continual doubling in the number of chromosome sets in every generation. Cells containing two sets of chromosomes are called diploid. Haploid cells contain one set of chromosomes. The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell is called its ploidy level.
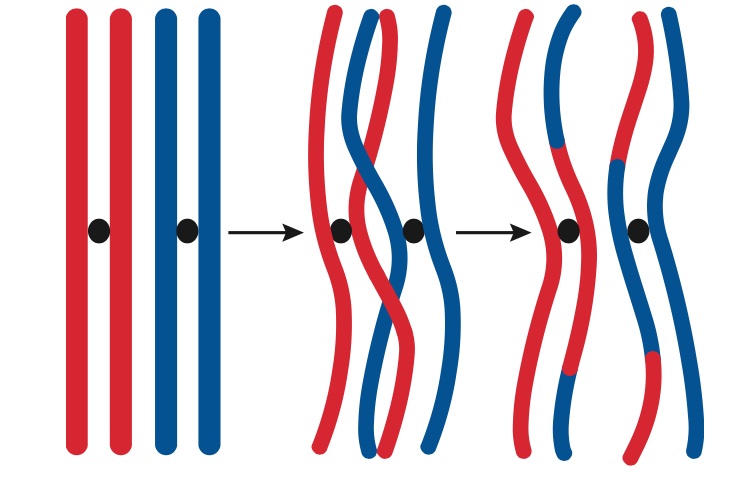
If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell contains two sets of chromosomes. Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms.
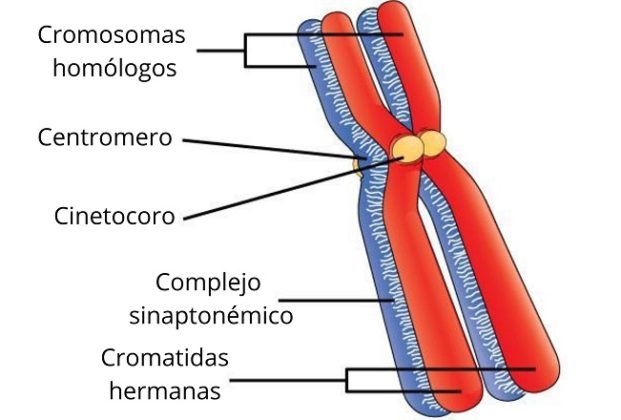
The result is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. \): Crossover occurs between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
